一. 前言
在前面的文章里,我们多次见到了中断的作用,如任务调度,系统调用从用户态陷入内核,文件系统的读写操作等。本文就Linux的中断机制进行较为全面的剖析。
二. 什么是中断
中断通常被定义为改变处理器执行指令的顺序的一个事件,该事件与CPU芯片内外部硬件电路产生的电信号相对应。中断通常分为同步中断和异步中断:
- 同步中断(synchronous):又称异常(exception),在指令执行时由CPU控制单元产生,之所以称之为同步,是因为只有在一条指令终止执行后CPU才会发出中断。异常通常又可以分为错误(Faults)、陷阱(Traps)和中止(Aborts)。
- 异步中断(asynchronous):即通常所说的中断(interrupt),由其他硬件设备依照CPU时钟信号随机产生。
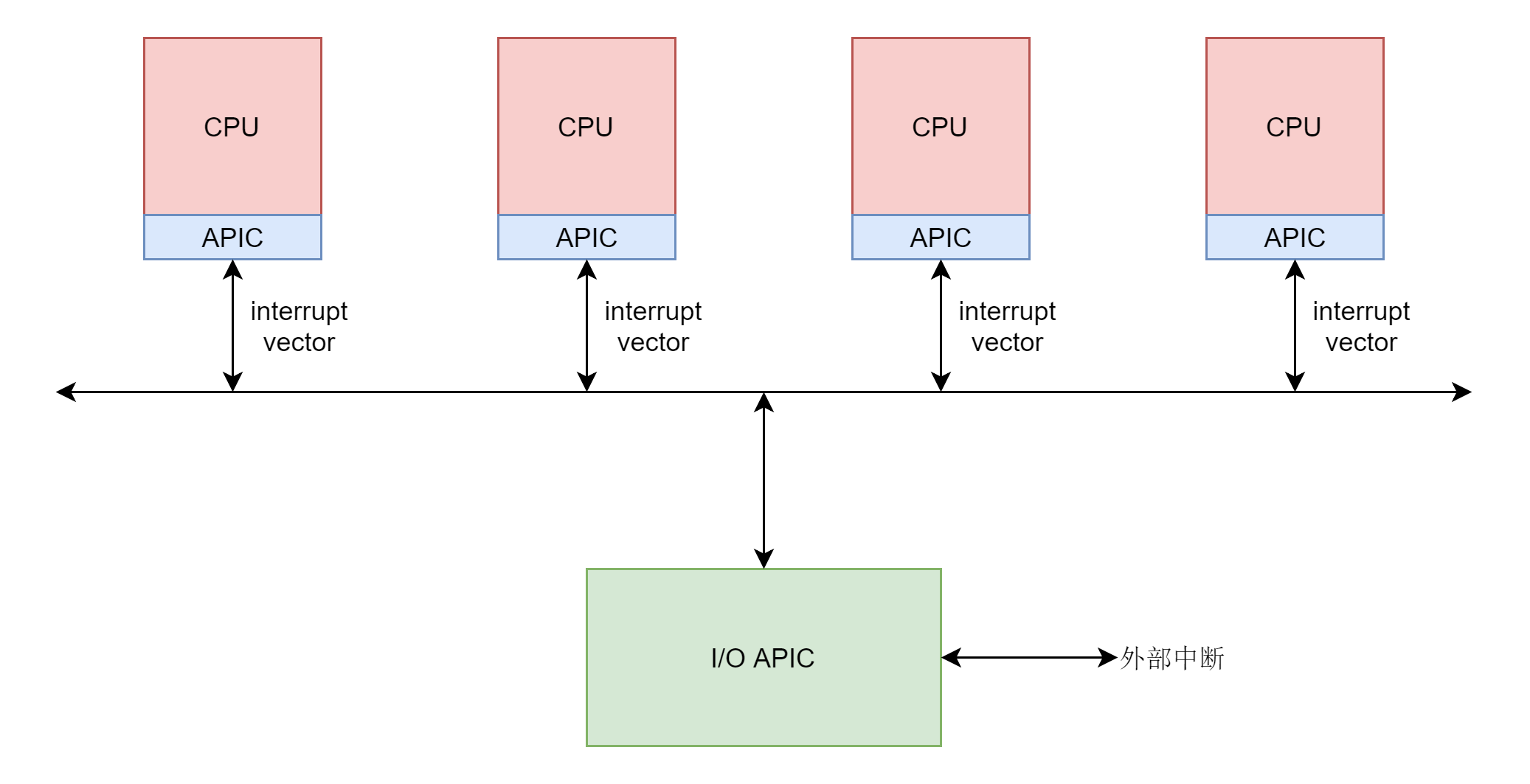
从另一个角度来说,我们可以把中断分为外部或者硬件引起的中断以及软件引起的中断两种。外部中断,由 Local APIC 或者与 Local APIC 连接的处理器针脚接收。第二种类型 - 软件引起的中断,由处理器自身的特殊情况引起(有时使用特殊架构的指令)。一个常见的关于特殊情况的例子就是 除零,另一个例子就是使用 系统调用(syscall)。假设每一个物理硬件都有一根中断线,设备可以通过它对 CPU 发起中断信号,中断信号先通过一个控制器,然后发到CPU上执行。比较原始的设备中,中断信号发送给 PIC ,它是一个顺序处理各种设备的各种中断请求的芯片。而现在通用的则是高级程序中断控制器(Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller)做这件事情,即我们熟知的 APIC。一个 APIC 包括两个独立的设备:
Local APICI/O APIC
第一个设备 - Local APIC存在于每个CPU核心中,Local APIC 负责处理特定于 CPU 的中断配置,常被用于管理来自 APIC 时钟(APIC-timer)、热敏元件和其他与 I/O 设备连接的设备的中断。
第二个设备 - I/O APIC 提供了多核处理器的中断管理。它被用来在所有的 CPU 核心中分发外部中断。
一个中断的发生流程如下:
- 外部设备给中断控制器发送物理中断信号
- 中断控制器将物理中断信号转换成为中断向量
interrupt vector,发给各个 CPU - 每个 CPU 都会有一个中断向量表,根据
interrupt vector调用一个 IRQ 处理函数 - IRQ 处理函数中,将
interrupt vector转化为抽象中断层的中断信号irq,调用中断信号irq对应的中断描述结构(IDT)里面的irq_handler_t
三. 软中断的必要性
上面我们分析了硬中断、软中断的概念以及中断的流程,但是为什么我们需要设计软中断呢?中断其实是一种异步的事件处理机制,可以提高系统的并发处理能力。由于中断处理程序会打断其他进程的运行,所以,为了减少对正常进程运行调度的影响,中断处理程序就需要尽可能快地运行。如果中断本身要做的事情不多,那么处理起来也不会有太大问题;但如果中断要处理的事情很多,中断服务程序就有可能要运行很长时间。特别是,中断处理程序在响应中断时,还会临时关闭中断。这就会导致上一次中断处理完成之前,其他中断都不能响应,也就是说中断有可能会丢失。
为了解决中断处理程序执行过长和中断丢失的问题,Linux 将中断处理过程分成了两个阶段,也就是上半部和下半部:上半部用来快速处理中断,它在中断禁止模式下运行,主要处理跟硬件紧密相关的或时间敏感的工作。下半部用来延迟处理上半部未完成的工作,通常以内核线程的方式运行。这也就是我们熟悉的硬中断和软中断了。
以网卡收包为例,网卡接收到数据包后,会通过硬件中断的方式,通知内核有新的数据到了。这时,内核就应该调用中断处理程序来响应它。对上半部来说,既然是快速处理,其实就是要把网卡的数据读到内存中,然后更新一下硬件寄存器的状态(表示数据已经读好了),最后再发送一个软中断信号,通知下半部做进一步的处理。而下半部被软中断信号唤醒后,需要从内存中找到网络数据,再按照网络协议栈,对数据进行逐层解析和处理,直到把它送给应用程序。
实际上,上半部会打断 CPU 正在执行的任务,然后立即执行中断处理程序。而下半部以内核线程的方式执行,并且每个 CPU 都对应一个软中断内核线程,名字为 “ksoftirqd/CPU 编号”,比如说, 0 号 CPU 对应的软中断内核线程的名字就是 ksoftirqd/0。不过要注意的是,软中断不只包括了刚刚所讲的硬件设备中断处理程序的下半部,一些内核自定义的事件也属于软中断,比如内核调度和 RCU 锁(Read-Copy Update 的缩写,RCU 是 Linux 内核中最常用的锁之一)等。
四. 中断结构体
对于每一个中断,我们都有一个对应的描述结构体irq_desc,其中包括了众多描述该中断特点的成员变量,这里尤其需要强调描述该中断对应的全部动作的变量struct irqaction *action。
1 | struct irq_desc { |
每一个中断处理动作的结构 struct irqaction,都有以下成员:
- 中断处理函数
handler - 设备 id
void *dev_id - 中断信号
irq - 如果中断处理函数在单独的线程运行,则有
thread_fn是线程的执行函数,thread是线程的task_struct。
一连串的动作通过链表的形式组合起来构成了该中断的所有动作。
1 | /** |
众多的中断irq_desc则采取类似于内存管理中所用到的基数树radix tree的方式进行管理。这种结构对于从某个整型 key 找到 value 速度很快,中断信号 irq 是这个整数。通过它,我们很快就能定位到对应的 irq_desc。
1 |
|
五. 中断流程
我们从 CPU 收到中断向量开始分析.CPU收到的中断向量定义于irq_vectors.h。下面这一段是该头文件的注释,详细描述了IRQ向量的基本信息:
- 单个CPU拥有256(8位)IDT,即能处理256个中断,定义为
NR_VECTORS - CPU处理的中断分为几类
- 0到31位为系统陷入或者异常,这些属于无法屏蔽的中断,必须进行处理
- 32到127位为设备中断
- 128位即我们常说的int80系统调用中断
- 129至
INVALIDATE_TLB_VECTOR_START也用来保存设备中断 INVALIDATE_TLB_VECTOR_START至255作为特殊中断
- 64位架构下每个CPU有独立的IDT表,而32位则共享一张表
1 | /* |
在前文中有分析内核的开始源于start_kernel(),而中断部分则开始于其中的trap_init(),这里会填写IDT描述符构成中断向量表
1 | void __init trap_init(void) |
在idt_setup_traps()中会初始化中断,其中前32个中断以枚举形式定义在arch/x86/include/asm/traps.h中
1 | /* Interrupts/Exceptions */ |
idt_setup_traps()实际调用idt_setup_from_table(),其参数为两个默认中断向量表,值和上面枚举值相同。
1 | /** |
在 start_kernel() 调用完毕 trap_init() 之后,还会调用 init_IRQ() 来初始化其他的设备中断,最终会调用到 native_init_IRQ()。这里面从第 32 个中断开始,到最后 NR_VECTORS 为止,对于 used_vectors 中没有标记为 1 的位置,都会调用 set_intr_gate() 设置中断向量表。used_vectors 中没有标记为 1 的,都是设备中断的部分,也即所有的设备中断的中断处理函数在中断向量表里面都会设置为从 irq_entries_start 开始,偏移量为 i - FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR 的一项。
1 | void __init init_IRQ(void) |
中断处理函数定义在 irq_entries_start 表里,在 arch\x86\entry\entry_32.S 和 arch\x86\entry\entry_64.S 都能找到这个函数表的定义。这里面定义了 FIRST_SYSTEM_VECTOR 到 FIRST_EXTERNAL_VECTOR 项。每一项都是中断处理函数,会跳到 common_interrupt() 去执行,并最终调用 do_IRQ(),调用完毕后,就从中断返回。
1 |
|
do_IRQ()从 AX 寄存器里面拿到了中断向量 vector,但是别忘了中断控制器发送给每个 CPU 的中断向量都是每个 CPU 局部的,而抽象中断处理层的虚拟中断信号 irq 以及它对应的中断描述结构 irq_desc 是全局的,也即这个 CPU 的 200 号的中断向量和另一个 CPU 的 200 号中断向量对应的虚拟中断信号 irq 和中断描述结构 irq_desc 可能不一样,这就需要一个映射关系。这个映射关系放在 Per CPU 变量 vector_irq 里面。
1 | /* |
在系统初始化的时候,我们会调用 __assign_irq_vector(),将虚拟中断信号 irq 分配到某个 CPU 上的中断向量。一旦找到某个向量,就调用irq_to_desc(irq)将 CPU 此向量对应的向量描述结构 irq_desc设置为虚拟中断信号 irq 对应的向量描述结构 。 do_IRQ() 会根据中断向量 vector 得到对应的 中断irq,然后调用 handle_irq()。handle_irq() 会调用 generic_handle_irq_desc(),最终调用 该中断irq绑定的处理函数 handle_irq()。
1 | bool handle_irq(struct irq_desc *desc, struct pt_regs *regs) |
handle_irq()函数最终会调用__handle_irq_event_percpu(),__handle_irq_event_percpu() 里面调用了 irq_desc ()里每个 handler,这些 handler 是我们在所有 action 列表中注册的,这才是我们设置的那个中断处理函数。如果返回值是 IRQ_HANDLED,就说明处理完毕;如果返回值是 IRQ_WAKE_THREAD 就唤醒线程。至此,中断的整个过程就结束了。
1 | irqreturn_t __handle_irq_event_percpu(struct irq_desc *desc, unsigned int *flags) |
总结
本文大致分析了中断的整个流程,由此我们可以了解到中断结构体,注册机制以及如何生效并触发对应的中断处理函数。
源码资料
[1] irq_desc
[2] trap_init()
[3] init_IRQ()
参考资料
[1] wiki
[3] woboq
[4] Linux-insides
[5] 深入理解Linux内核
[6] Linux内核设计的艺术
[7] 极客时间 趣谈Linux操作系统
[8] Linux设备驱动程序

